Instability in the ulnar carpal wrist may present with pain, swelling, and tenderness in the ulnar aspect of the wrist. Instability due to weakened or rupture ligaments, can occur between the ulna and the carpus, the lunate-triquetral joint, and/or the triquetrohamate joint.
The following describes a few important assessments to assist clinical evaluation of ulnar sided wrist pain when the symptoms are suspected to be related to ulnar carpal instability.
Assessments for Clinical Evaluation of Ulnar-Sided Wrist Pain
1. Relocation Test
The relocation test involves the combination of carpal pronation and anterior to posterior glide of the carpus on the ulna. This test realigns the carpus when ulnocarpal instability causes volar sag and supination of this aspect of the wrist usually due to laxity or tear of the ulnocarpal ligaments or the triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC). This test is positive if wrist pain is reduced with this maneuver.
2. Pisiform Boost Test
The pisiform boost test involves placing the wrist in passive ulnar deviation and then applying volarly directed pressure to the ulna and dorsally directed pressure to the pisiform. This test is positive if it reduces pain, occurs with laxity or there is clicking suggestive of involvement of the ulnar wrist structures.
| How to Treat TFCC - Symptoms & Causes of Ulnar Sided Wrist Pain- View Video |
3. Midcarpal Shift Test (also known as Catch-Up Clunk Test and Pivot Shift Test)
The midcarpal shift test involves placing a volarly directed load over the capitate and then ulnarly deviating the wrist with simultaneous axial load. The test is positive if it produces a painful clunk or reproduces pain. This test could indicate midcarpal instability which occurs due to ligament laxity and often causes a volar sag on the ulnar wrist with clunking during movement from radial to ulnar deviation. With the hand pronated, press palmarly (downward) on the capitate. Apply and hold an axial distraction of the hand while you passively pull the wrist into ulnar deviation. A painful and often audible clunk or pain response is considered a positive response
4. Ballotment Test for Lunate-Triquetral (LT) Instability
The ballotment test can check for instability between the LT joint when there is injury or laxity of the ligaments between these two bones. The lunate should be stabilized while volar and dorsal pressure is applied to the triquetrum. This test is positive if it elicits pain, clicking or laxity.
Treatment for Ulnar Carpal Instability
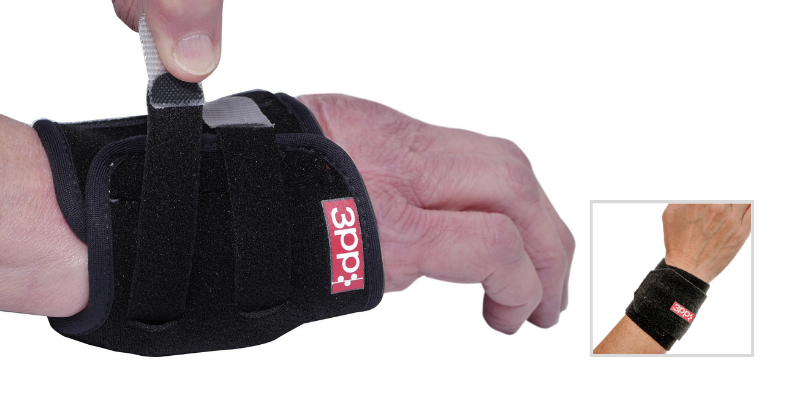
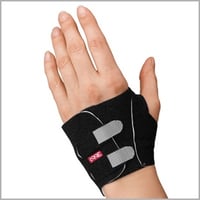
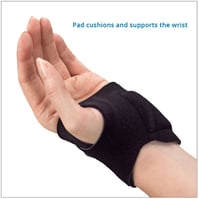
If an ulnar carpal instability is detected with one of the above clinical evaluations, using the 3pp Carpal Lift or the 3pp Wrist POP Splint can assist ulnar wrist stabilization via providing a dorsal pressure to the ulnar head or a volar pressure to the ulnar carpus.
The 3pp Carpal Lift incorporates a pad under the ulnar carpus and adjustable straps adding a dynamic lift without pressure on the ulna.
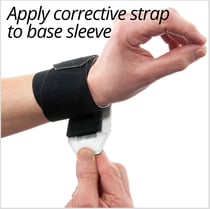
The 3pp Wrist POP Splint has a corrective strap and pressure pads that allow the user to position force across the distal ulna and radius to restore stability for pain-free supination / pronation and wrist motion.