Anatomy of the Wrist
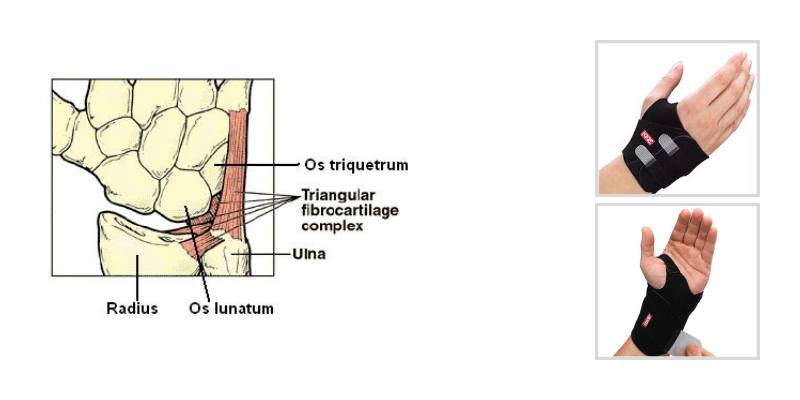
The triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) is a complicated component of the wrist comprised of several ligaments, an articular disc, a meniscus homolog and the sheath for one of the extensor tendons that crosses the ulnar wrist. To say this more simply, the TFCC is a cartilaginous and ligamentous structure that runs from the ulnar side of the distal radius, across the distal aspect of the ulna, and connects the ulna to the ulnar sided carpal bones (lunate and triquetrum) at their proximal aspect.| Are you a patient or consumer? Click Here to learn more about TFCC on our consumer site |
Function of TFCC
As may be suggested via the anatomy of the TFCC, its function is to provide stability to both the distal radioulnar joint (DRUJ) and the ulnar carpus. It also transmits 20% of an axial load applied from the ulnar carpus to the distal ulna.
Injury to the TFCC
An injury to the TFCC may be suspected with presentation of ulnar-sided wrist pain and decreased strength. An injury to this structure may also cause symptoms of a painful click with forearm rotation, pain with ulnar deviation, and/or snapping and popping at the ulnar wrist.
Physical Exam of the TFCC
A new or acute injury to the TFCC may present with edema local to the ulnar aspect of the wrist and tenderness with palpation of the TFCC at the ulnar wrist just distal to the ulna. A load can be applied to the TFCC via ulnarly deviating the wrist and adding an axial load. Replication of pain with this maneuver can mean an injury to the TFCC. A significant injury to the TFCC can cause instability at the DRUJ. To check for this, hold the patient’s forearm in neutral, stabilize the distal radius in one hand and use the other hand to move the ulna forward and back. Greater movement on the involved side in comparison to the non-involved side may indicate instability.
Diagnosis of an Injury to the TFCC
It is common that an individual with an injury to the TFCC has a history of a fall on an outstretched hand, a traction injury to the ulnar wrist, or gripping coupled with forearm rotation. We can suspect an injury to the TFCC with the use of the clinical signs noted above; however a tear is confirmed during visualization in surgery or using an MRI.
Treatment for TFCC Injuries
Treatment for TFCC injuries depends in part on the extent of the injury and the particulars on the components of the TFCC that are involved. Conservative treatment from a therapist initially involves support and rest to the involved structures prior to addressing range of motion and strength. Likewise, post-operative hand therapy may involve support to the TFCC. Support can be as involved as a custom thermoplastic orthosis that limits wrist and forearm motion or as minimal as a strap that provides support to the DRUJ and ulnar carpus (as the TFCC does).
The 3pp Wrist POP Splint applies adjustable compression over the distal ulna and a counterpoint of pressure under the distal radius for stability and effective treatment. The 3pp Carpal Liftt adds compression and a dynamic lift without pressure on the ulna.
There are several options for orthoses to provide support to the wrist following an injury to the TFCC, including the 3pp Wrist Wrap NP for support without full immobilization.