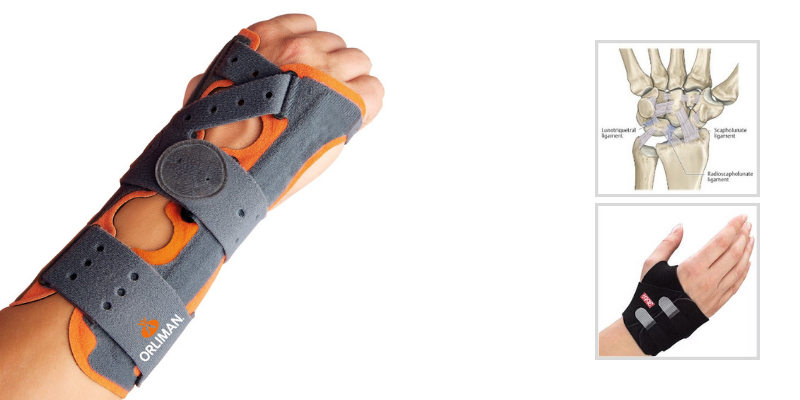
Anatomy of the Wrist
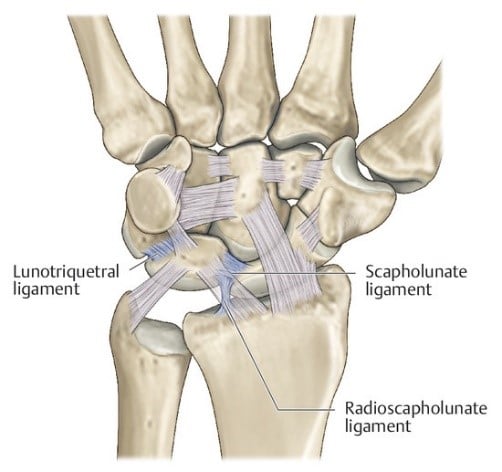
The lunate and the triquetrum make up the ulnar side of the proximal carpal row at the wrist. Ligaments, particularly the lunotriquetral (LT) ligament, provide support to this joint. This ligament is horse-shoe or c-shaped and contains a volar, dorsal and proximal component.
Function of the Wrist
The LT ligament assists with providing stability to the proximal carpal row and allowing the carpal bones (most significantly the lunate and triquetrum) to move in appropriate coordinated motion. Specifically, the ligament works as a rotational constraint and to transmit extension movement of the triquetrum.
Lunotriquetral Dissociation Injury
A Lunotriquetral Dissociation may occur due to a fall backwards on an outstretched hand with the arm externally rotated, the forearm supinated, and the wrist is extended and radially deviated. This motion causes stress between the LT joint and can cause tearing of the fibers of the LT ligament. LT injuries may result in ulnar sided wrist pain, painful crepitation in ulnar deviation, point tenderness over the dorsal LT joint, weakness, and a feeling of instability with supination, ulnar deviation, and extension of the wrist. If the injury is significant enough, the ulnar portion of the carpus may appear to sag volarly from the distal ulna with visual inspection.
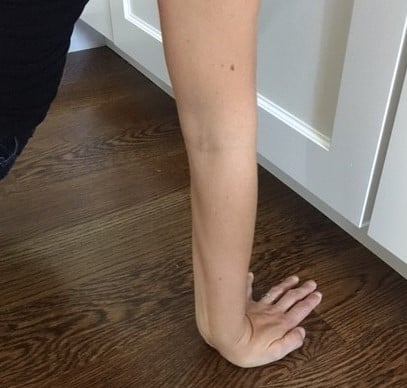
Physical Exam of LT Injury
Most commonly, clinical examination involves the ballottement test when a LT injury is suspected. To perform this test, use one hand to hold onto the lunate, and with your other hand move the triquetrum in a volar and dorsal manner (checking the status of the ligamentous support between the bones). The test is positive when it reproduces pain and involves increased motion compared to the non-involved side.
Diagnosis of LT Dissociation
If a LT dissociation is suspected, radiographs may reveal a change in alignment of the proximal carpal row. However, an injury to the LT ligament may not always occur with radiographic changes, so an MRI may be needed to check the status of the ligament.
Treatment of LT Dissociation
Depending on the details of the injury to the LT ligament and the individual with the injury, a LT dissociation may be treated with surgical repair or reconstruction or by conservative means. Conservative treatment involves immobilization with a static wrist orthosis or use of a product to assist with boosting the pisiform (which is just volar to the triquetrum) to provide external support to the LT joint. In addition, conservative treatment of these injuries involves proprioceptive re-education and strengthening of the muscles that help stabilize the wrist.
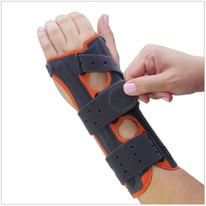
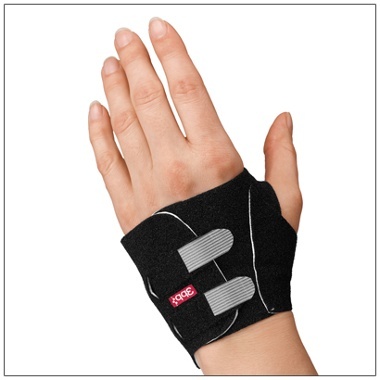
There are several options for orthoses to provide support to a wrist with a possible LT dissociation. These products include the Fix Comfort Wrist Brace for wrist immobilization and the 3pp Carpal Lift or the 3pp Wrist POP designed to provide a boost to the pisiform at the volar triquetrum.
 |
 |
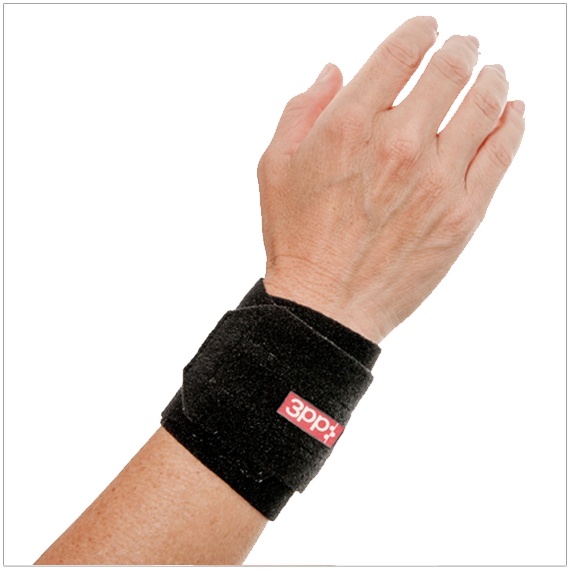 |
| Fix Comfort Wrist Brace | 3pp Carpal Lift | 3pp Wrist POP |