The Problem with the Distal Radioulnar Joint
How to restore the rhythm of the radius and ulnar without constraining motion:
Loss of TFC integrity leads to instability of the DRUJ disrupting the rhythm of the radius as it travels around the ulnar styloid. This blog describes how a properly designed orthosis can be employed to restore stability without disrupting the rhythm of the rotating radius.
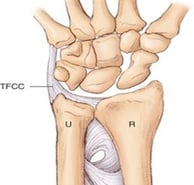
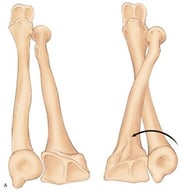
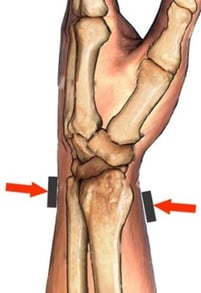
The TFC is the primary stabilizer of the DRUJ The “pirouette” of the radius around the ulna
The Answer for Treatment
To restore stability, apply basic orthotic principles of pressure distribution and application of force for the most adjustable and successful design option.
When choosing an orthotic option, adhere to the basic principles:
Pressure Distribution
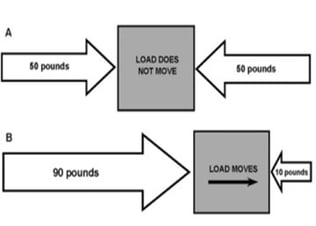
P = force /area of application
Points and Direction of Force
Minimum of 2 pts. required to stabilize rotation
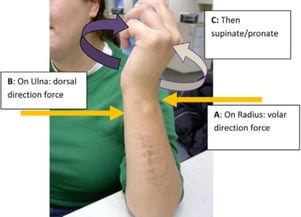
It's important to choose a design that distributes pressure and allows the wearer to alter the degree and direction of force to: “Provide a counterforce which mimics the stabilizers to seat the ulnar head in the sigmoid notch with just enough force to position the joint in its anatomical position.”1
VH O’Brien, J Thurn “A simple distal radioulnar joint orthosis” J Hand Ther 26 (2013) 287-290 Elsevier
THIS NOT THIS

Three Orthotic Principles
The following are the pros and cons of three orthotic designs.
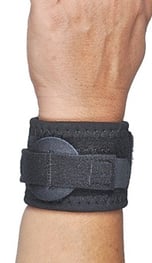
Orthotic Design: Option 1 of 3
Circumferential wrap directing equal force medially to prevent “separation” of the ulna and radius
Pro: Ease of application
Con: Does not allow adjusting the direction of force
Con: Circumferential force may compress the ulna into the sigmoid notch

Wrist WidgetTM
Medically directed force = compression of the ulna into the sigmoid notch
Orthotic Design: Option 2 of 3
Circumferential wrap with a single point of force palmarward over or around the ulnar styloid
Pro: Ease of application, comfort
Con: Lacks counterforce and the ulnar pad or donut may be misaligned on the ulnar styloid
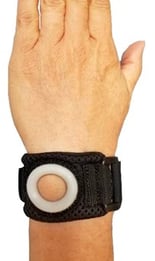
Squeeze Ulnar Compression Wrap Bullseye Wrist Band
Lack of counterforce applies majority of force on the ulna and constrains the radius
Orthotic Design: Option 3 of 3
A corrective strap and compression pads applied over a non-slip base sleeve offer adjustable counterforce force palmarly on the ulnar styloid and dorsally on the radial styloid
Pro: Wearer can locate and balance counterforce according to comfort
Con: Requires proper positioning of counterforce pads
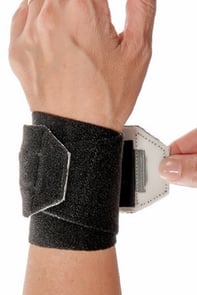
3pp Wrist POP (Point of Pressure)
The 3pp® Wrist POP™ both adheres to orthotic principles and avoids circumferential force. Both the direction and degree of force can be varied by altering the location and thickness of corrective pads. Non-slip foam lining eliminates over tightening and breathable material is comfortable for long-term wear.
For more information on the 3pp Wrist POP click on the button below