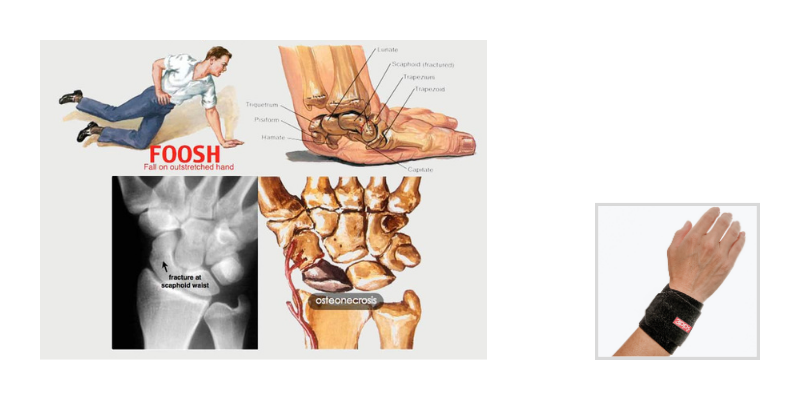
A traumatic fall on an outstretched hand, commonly referred to as a FOOSH injury, can result in a wide range of wrist injuries. While the most well-known FOOSH injury is a distal radius fracture, which is typically identified and treated first by a physician, other wrist injuries may be less obvious and present later as persistent pain or dysfunction.
As a healthcare professional, you may be seeing an increase in referrals for wrist pain following falls. This makes it a good time to review key clinical signs and tests used to identify common FOOSH-related wrist injuries beyond fractures.
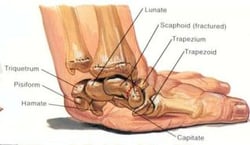
Common FOOSH Wrist Injuries
Scaphoid Fractures
Scaphoid fractures occur with wrist hyperextension combined with radial deviation. The scaphoid is located in the anatomical snuffbox on the radial side of the wrist, near the base of the thumb. One challenge with scaphoid fractures is that they do not always appear on initial radiographs, making clinical assessment especially important.
Clinical signs that may indicate a scaphoid fracture include:
-
Localized tenderness with palpation of the scaphoid
-
Pain with axial compression of the thumb
-
A history of a fall onto a hyperextended wrist
-
Persistent radial-sided wrist pain despite normal initial imaging
| Are you a patient or consumer? Click Here to view wrist braces on our consumer site |
Scapholunate (SL) Ligament Injury
An injury or tear to the scapholunate (SL) ligament can occur following a FOOSH or any sudden load placed on the wrist. SL ligament injuries commonly present with dorsal radial wrist pain and swelling.
Helpful clinical signs for suspected SL ligament injury include:
- Palpation just distal to Lister’s tubercle on the dorsal radius, with sharp localized pain
- A positive scaphoid shift (Watson) test
To perform the scaphoid shift test:
1. Apply pressure to the volar prominence of the scaphoid while moving the wrist from ulnar deviation to radial deviation with slight wrist flexion.
2. A painful clunk with symptom reproduction when pressure is removed is usually indicative of a ligament injury, but be sure to check the non-involved side for baseline ligament laxity information.
Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex (TFCC) Injury
A TFCC injury may occur during a FOOSH involving excessive forearm rotation and is a common source of ulnar-sided wrist pain.
When TFCC injury is suspected, two commonly used clinical tests include:
1. Ulnar Fovea Sign
Apply pressure between the ulnar styloid process and the flexor carpi ulnaris tendon, as well as between the ulnar head and pisiform
The test is positive if it reproduces the patient’s pain
2. TFCC Load Test
Load the wrist in ulnar deviation
Move the wrist volarly and dorsally
A positive test reproduces pain or symptoms
Support Options for FOOSH-Related Wrist Pain
Following a FOOSH injury, individuals may experience wrist pain related to strains, sprains, post-operative recovery, or post-casting.
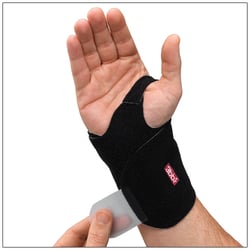
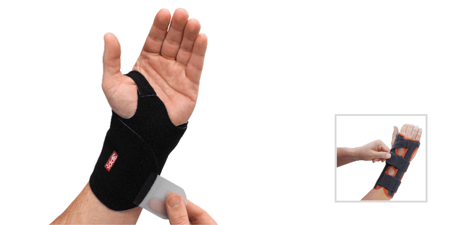
The 3pp Wrist Wrap NP and the 3pp Wrist POP are examples of wrist supports designed to help stabilize the wrist while allowing functional movement during recovery.
3pp® Wrist Wrap NP: Designed to provide comfortable compression and support for wrist strains, sprains, and post-injury use.
3pp® Wrist POP Splint: Offers targeted support for wrist instability and ulnar-sided wrist pain, commonly associated with FOOSH injuries.
Supporting Recovery After a FOOSH Injury
Early recognition of FOOSH-related wrist injuries is essential for guiding appropriate treatment and preventing long-term pain or instability. When fractures have been ruled out, a thorough clinical evaluation can help identify ligamentous or soft tissue injuries that may otherwise be overlooked. Timely intervention, combined with appropriate support and rehabilitation, can play an important role in restoring function and helping individuals return to daily activities safely and confidently.
For Patients and Consumers
If you’re experiencing wrist pain after a fall or injury, wrist braces may help provide comfort, support, and stability during recovery. Learn more on our consumer site OMA.
Blog References: Click to see the references for this blog post