The Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex (TFCC) is a group of ligaments and cartilage on the ulnar side of the hand. The TFCC ligaments attach the cartilage to the small wrist bones which also suspend the ends of the two forearm bones, the ulna and the radius.
TFCC Wrist Injuries
- Trauma: A fall on an outstretched hand (commonly referred to as a "FOOSH") is a frequent cause.
- Degeneration: Overuse or the natural aging process can lead to wear and tear of the TFCC.
- Athletic Activities: Athletes, particularly gymnasts and others who bear weight on their hands, are at higher risk due to repetitive stress on the wrist.
Diagnosing TFCC Injuries
Accurate diagnosis is essential, as TFCC injuries are often misdiagnosed as a generic "wrist sprain." Key symptoms to look for include:
- Ulnar-Sided Wrist Pain: Pain localized on the pinky side of the wrist, especially during gripping or weight-bearing activities (e.g., pushing off a chair).
- Clicking or Popping Sounds: Audible or palpable sensations when moving the wrist or rotating the forearm.
- Reduced Functionality: Difficulty with wrist motion, particularly supination and pronation.
Treatment Options for TFCC
TFCC problems can be very persistent. In most cases, TFCC tears are managed with anti-inflammatories and splinting for about four weeks followed by corticosteroid injections if necessary. After splinting the wrist for a period of time to reduce symptoms, range of motion exercises can be recommended to restore motion and strengthening.
1. Initial Management:
- Anti-Inflammatory Medications: To reduce pain and swelling.
- Splinting: Immobilize the wrist for approximately four weeks to allow healing.
- Corticosteroid Injections: Considered if symptoms persist after initial treatment.
2. Rehabilitation:
- Range of Motion Exercises: Gradually restore wrist mobility after the splinting period.
- Strengthening Exercises: Focus on stabilizing the wrist and forearm muscles to prevent recurrence.
Splinting Solutions for TFCC
Specialized splints can provide targeted support and pain relief for TFCC injuries. Two effective options include:
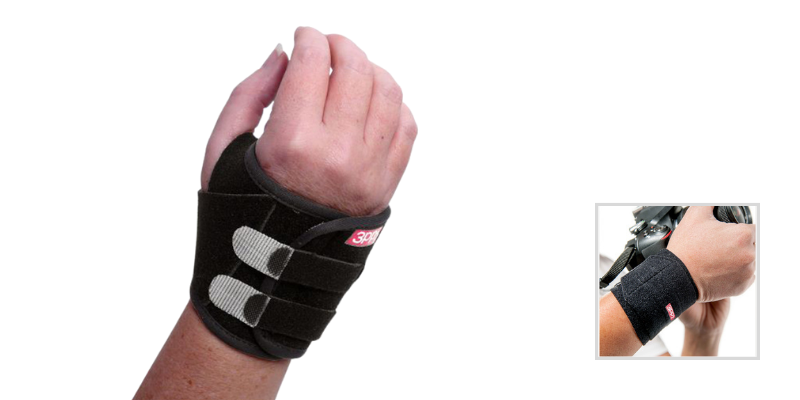
1. The 3pp Carpal Lift reduces wrist pain and popping by supporting the ulnar carpal bones.
- Designed to reduce wrist pain and popping by supporting the ulnar carpal bones.
- Features a padded palm cushion and dual straps to realign the wrist and relieve stress on the TFCC.
- Ideal for incomplete tears where surgery is not required or is delayed.
- Can easily be strapped on with one hand, and may be worn during activity
2. The 3pp Wrist POP Splint is an effective treatment of TFCC injuries, ulnar-sided wrist pain, and distal radioulnar joint (DRUJ) instability.
• Provides adjustable compression over the distal ulna and counterpressure under the distal radius for enhanced stability.
• Includes corrective straps and pressure pads to restore stability, enabling pain-free supination, pronation, and wrist motion.
• The foam-lined base sleeve ensures a secure fit without slipping or rolling.
When Surgery Is Needed
Surgical intervention may be necessary for severe TFCC tears, particularly those involving fractures or significant instability of the distal radioulnar joint (DRUJ). However, conservative treatment is often sufficient for the most common types of TFCC injuries.________________________________________