Wrist pain, particularly on the ulnar side, can be frustrating and painful for patients, often signaling an injury to the triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC). This complex structure plays a critical role in wrist stability and functionality. Understanding the anatomy, diagnosis, and treatment of TFCC injuries is key to improving patient outcomes when managing ulnar-sided wrist pain.
Anatomy of the Wrist
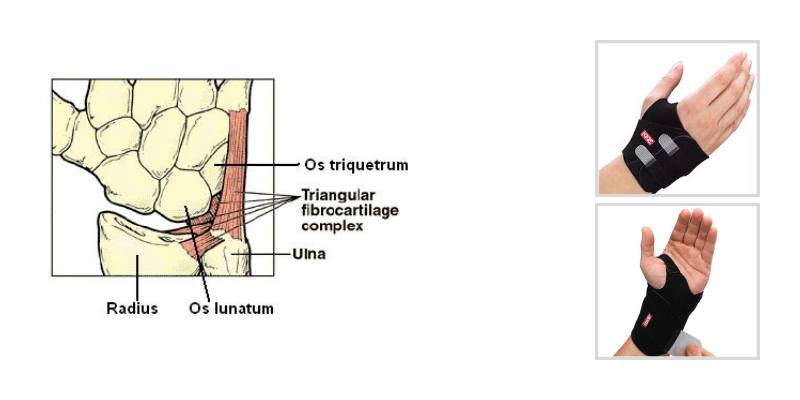
The TFCC is an intricate structure made up of several components:
- Ligaments
- An articular disc
- A meniscus homolog
- The sheath for an extensor tendon on the ulnar wrist
To simplify, consider the TFCC as a network of cartilage and ligaments. It runs from the ulnar side of the distal radius (the outer forearm bone) across the distal ulna (the inner forearm bone) and connects to the proximal ulnar-sided carpal bones (the lunate and triquetrum). This structure acts as a crucial stabilizer for the wrist and forms a solid connection between the ulna and the carpal bones, ensuring smooth wrist motion.
| Are you a patient or consumer? Click Here to learn more about TFCC on our consumer site |
Function of TFCC
The TFCC has two primary roles:
1. Stabilization
It stabilizes the distal radioulnar joint (DRUJ) and the ulnar carpus, supporting wrist movements like pronation and supination.
2. Force Transmission
The TFCC bears about 20% of the axial load transmitted between the ulnar carpus and the distal ulna during wrist activities like gripping and weight-bearing.
Understanding its function highlights just how vital the TFCC is—not only in distributing forces across the wrist but also in maintaining its integrity and mobility.
Recognizing a TFCC Injurynjury to the TFCC
An injury to the TFCC may present with the following symptoms:
- Pain on the ulnar (pinky) side of the wrist
- Decreased grip strength or difficulty lifting objects
- A painful click or snapping sensation during forearm rotation
- Pain exacerbated by ulnar deviation (bending the wrist towards the pinky)
Physical Exam of the TFCC
To identify a potential TFCC injury, targeted physical examination techniques can be used:
- Edema: Check for swelling localized at the ulnar wrist.
- Tenderness: Palpate the TFCC area just distal to the ulna for tenderness.
- Pain Replication Test: Apply an axial load to the TFCC by combining wrist ulnar deviation with compression. Pain in this position suggests an injury.
- DRUJ Instability Test: To check for this, hold the patient’s forearm in neutral, stabilize the distal radius in one hand and use the other hand to move the ulna forward and back. Greater movement on the involved side in comparison to the non-involved side may indicate instability.
Diagnosis of an Injury to the TFCC
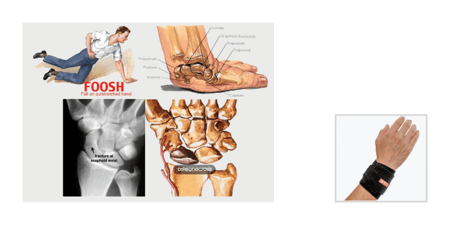
It is common that an individual with an injury to the TFCC has a history of a fall on an outstretched hand, a traction injury to the ulnar wrist, or gripping coupled with forearm rotation.
While clinical signs offer strong clues, definitive TFCC injury diagnosis typically requires magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or visual confirmation during arthroscopic surgery.
Treatment for TFCC Injuries
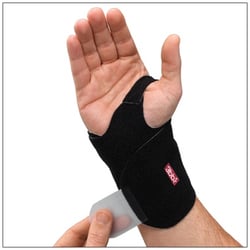
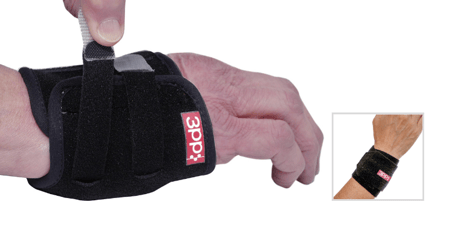
Treatment for TFCC injuries depends in part on the extent of the injury and the particulars on the components of the TFCC that are involved. Conservative treatment from a therapist initially involves support and rest to the involved structures prior to addressing range of motion and strength. Likewise, post-operative hand therapy may involve support to the TFCC. Support can be as involved as a custom thermoplastic orthosis that limits wrist and forearm motion or as minimal as a strap that provides support to the DRUJ and ulnar carpus (as the TFCC does).
The 3pp Wrist POP Splint applies adjustable compression over the distal ulna and a counterpoint of pressure under the distal radius for stability and effective treatment. The 3pp Carpal Liftt adds compression and a dynamic lift without pressure on the ulna.
There are several options for orthoses to provide support to the wrist following an injury to the TFCC, including the 3pp Wrist Wrap NP for support without full immobilization.
Understanding TFCC injuries involves recognizing their complex anatomy, assessing patients through targeted physical exams, and implementing effective treatment strategies. The involvement of therapeutic tools like orthoses ensures that patients not only recover but can return to their daily activities with confidence.